Nuts, Oils and Fat
Lets talk nuts for a minute?
What are some of the benefits you get from different nuts?
Almonds “ calming nut”
lower cholesterol
lower the risk of heart disease
contain magnesium- great for calming the nervous system
stabilise blood glucose levels
contain copper, manganese and the antioxidant Vitamin E
rich in monounsaturated fats, fibre antioxidants and riboflavin
great for melatonin production ( take with pistachios)
Cashews “ balance nut”
lower cholesterol
lower the risk of heart attack/heart disease
good for mood
contain Vitamin E, Vitamin K and B6
assists in weight loss
contain magnesium, iron , selenium, copper, phosphorus, zinc
Walnuts “brain nut”
good for most things from bone health to cancer
balance blood glucose
support arterial function
good for brain health - shown to be neuroprotective and enhance memory function
good source of omega 3 (ALA)
lowers LDL cholesterol and is rich in magnesium
boast the highest phytochemical, flavonoid and antioxidant capacity amongst tree nuts
Rich source of fibre, protein
Pecans “ anti-inflammatory nut”
high in manganese and copper, calcium, magnesium and potassium.
as powerful as walnuts in terms of antioxidant capacity.
help balance triglycerides and cholesterol
Brazil nuts “ anti-aging nut”
high levels of selenium- good for nails, hair and skin & thyroid
good for metabolism, digestive health and thyroid function
help with detoxification- liver function
protect against arthritis
Hazelnut “ cardiovascular nut”
good for endothelial function
keep LDL cholesterol from oxidising
double the antioxidant capacity of almonds
great source of iron
Pistachio “sleep nut”
abundant in arginine- amino acid
rich in folate- important for energy and hormone health
rich in potassium ( 3x more per gram than bananas)- good for cramps and fatigue
produces nitric oxide which improves arterial function and blood flow
great for supporting melatonin production ( take with some almonds 1-2hrs before bed)
Macadamia “ superfood beauty nut”
contain same amount of monounsaturated fats as olive oil.
improve overall cholesterol
stabilises blood glucose levels
reduces hunger and good for weight loss
reduces Alzheimer risk
contains: protein, fiber, thiamine, magnesium, B6, iron, manganese, Selenium, Vit A, Vit E and copper
is an antioxidant
Good Fats:
Nuts
Seeds
Fatty, Cold water fish
Fatty grassfed pastured meat
Olives
Avocado
Eggs
Coconut
Tell me more about fats? Why would I eat them?
Unlike carbohydrates and protein, fat does not stimulate the release of insulin (a fat storing hormone) and slows gastric emptying and stimulates the release of peptide YY to emulsify fats via activation of cholecystokin (CKK).
Fats also increase satiety (fullness) as they decrease gherlin, they are important for your absorption of your fat soluble vitamins (A,D,E,K) the proper function of your nerves/brain, proper hormone production and cell communication. The length of the fatty acid chain does impact on how much it will increase hormonal signalling in the gut and ghrelin response. If you aren’t eating fats you can develop Essential Fatty Acid deficiency.
What are the signs of Essential Fatty Acid (EFA) deficiency?
dry skin
cracked skin on heels and fingertips
hair falling out
lifeless hair or dandruff
slow wound healing
depression, lack of motivation
irritability
soft or brittle nails
allergies
high blood pressure
dry eyes
aching joints
fatigue
difficulty loosing weight
arthritis
pre-menstrual syndrome (PMS)
mentrual irregularities
painful breasts
As a general rule of thumb, avoid industrialised manmade fats/oils and opt for whole food fats. Here are fats worth incorporate into your diet:
Coconut oil- is made up of medium chain triglycerides, most of which are comprised of caprylic acid and auric acid. Caprylic acid and auric acid are potent antimicrobials, meaning they naturally kill unwanted bacteria, viruses and fungi.
Olives- rich sources of monounsaturated fats and contain the powerful antioxidant oleocanthal. Olives are anti-inflammatory and have been shown to be beneficial for cardiovascular health.
Sardines- high in anti-inflammatory long chain omega 3 EPA and DHA fats for brain health and cardiovascular support, high in protein, rich in B12, selenium, Vit D, phosphorus, calcium and lowest mercury of all fatty fish.
Flaxseed- rich in polyunsaturated LA Omega-3 fats, flavonoids, high in lignans which act as antioxidants and as an insoluble fibre. Can modulate oestrogen levels (used in seed cycling) and also has blood pressure lowering benefits.
Pumpkin seeds- is the only seed that is alkaline forming, high in protein, rich in zinc, lignan’s and phytosterols.
Avocado oil- high in healthy monounsaturated fat, low in fruit sugar, rich in potassium, rich in fibre, source of Vitamin K, folate, magnesium, lutein and zeaxanthin.
Hemp seed- rich in both ALA Omega 3 and Omega 6 essential fats also rich in protein 10g complete protein per serving.
Chia seed, pumpkin seed, flaxseed, walnuts all have Omega 3 SCFA (short chain fatty acids in them. Where as Algae and cold water fish have Omega 3 LCFA (long chain fatty acids).
Can I cook with any of the good oils?
The oils you want to cook with need a high heat tolerance point/ smoking point. This tends to be more of your saturated/mono-saturated fats like coconut oil, grapeseed oil, avocado oil etc. Rather than oils like olive oil which burns and can rancify (oxidise) meaning you won’t get the benefits from that fat- it is better as a salad dressing or on low heat not high heat temperatures.
If you are eating foods high in Omega 6 its important to remember even if you are adding in lots of Omega 3 fats, Omega 6 will block the absorption of omega 3. There are only enough chairs for everyone to sit at the table and omega 6 tends to get to the table first.
Eating daily flaxseed or hemp oil gives you a combination of Omega 3-6-9.
Fish oil is also a good alternative but I’ll talk about the additional benefits of eating salmon another time.
Omega 6 is bad right and Omega 3 is good?
When talking about Omega 3 and Omega 6 it's not black and white-this one is good and this one is bad. Omega 3 and Omega 6 are classed as PUFAs (polyunsaturated fatty acids)and are vital to pretty much every component of the human cell. The body needs them to balance out hormones, insulate nerves, keep the skin and arteries supple, to keep the body warm etc.
Fat Basics
Fats are wither saturated or unsaturated
Staurated: Animal, coconut,palm oil ( think of fats that are hard at room temperature)
Mono-saturated: Olive, avocado, peanut, macadamia
Polyunsatirated: fish oil, seeds, nuts, flaxseed, walnuts ( are usually liquid pils at room temperature)
Phosphlipids: Eggs, Soybeans
Sterols: Meats, egg, fish, chicken, dairy
Lipids dissolve well in alcohol as its a lipid
Trans fatty acids: alter structures and cause the same damage as saturated fats. They resist desaturation and elpngation and are more like monunsaturated fats than poly unsaturated fats.
Triglycerides- as animal are soldi- they are long chains, stable and dont go rancid like short chain fatty acids do.
Vitamin E helps stop fats from going rancid
Your body actually stores most fat as triglycerides ( 3 fatty acids and glycerol together).
25% of total fat in your body comes from diet ONLY the rest is what your body makes.
Cholesterol is either esterifed or unesterified and 50% of the cholesterol consumed is unesterified.
Fats need protein to be transported in your body as they are hydrophobic ( scared of water and blood is essentially water).
Essential fatty acids
Are Omega 3 + 6 -we cant make these ourselves
Ideal ratio is 4:1 of Omega 6 to Omega 3 but the modern diet is more like 20:1!
We often dont need to decrease omega 6 but increase Omega 3
Vegetarians and Vegans are often more efficient at converting plant sources due to the lack of meat in their diets than meat eater are. That is the conversaion of Omega 6 to Omega 3.
If your diet is high in trans fatty acids then this reduces Omega 3 and Omega 6 absorption.
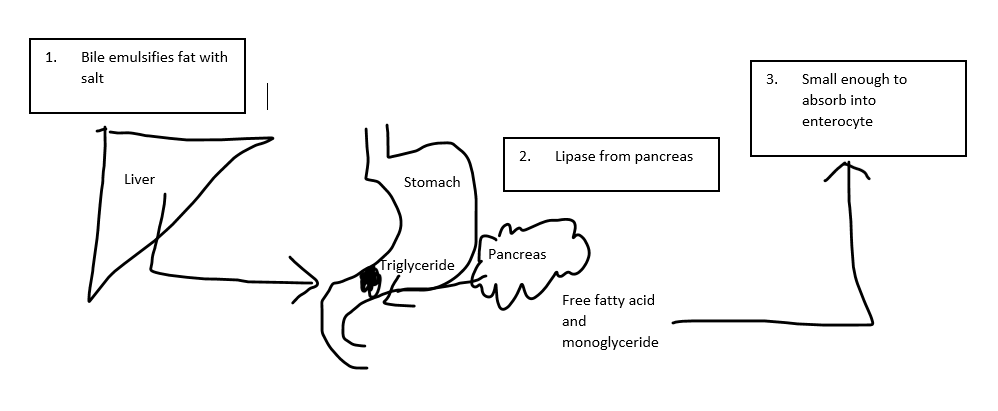
Image represents: Fat break down process with digestion and transport
*Lipase- is an enzyme that emulsifies (breaks down fat)
**:Bile is made by the liver and stored in the gall bladder.
Transport proteins in enterocytes (liver cells) bring unesterified cholesterol across the cell wall (C1-like protein). If thre is too much cholesterol than another protein (ATP binding cassette binding protein) help transport it to the lumen of the gut from the liver so that it can be excreted in faeces.
Free fatty acid + monoglyceride form a triglyceride in the enterocyte. Chlomicron (phospholipid layer+protein+triglyceride esterified + unesterified) enters the blood so it can be deposited as fatty acids to the muscles or fat cells ( it is the transporter).
Chylomicron remnants ( left over chylomicron after it has dropped off fats around the body)- the liver then breaks down into esterifed cholesterol which is stored and unesterified which is further converted into bile, VLDL and HDL.
Mevalonate pathway- to make cholesterol
The trouble with LDL on lab results
Tells you how many are present but doesn’t tell you the size or number of particles that make it up.
The higher the particle amount the higher the cardiovascular risk If the LDL cholesterol level is high and the LDL particle size is high this is predictive of cardiovascular disease. However is one is high and the other is low this is not.
There are even things call VLDL ( very low density lipoproteins) and these are synthesized by the liver and act like chylomircon and can be turned into LDL.
Small doesn’t always mean better the smaller the LDL particle the easier it is for it to get past the endothelial (cell lining) and into smooth muscle to cause atherosclerosis (fatty deposits that can block arteries).
Now it’s important to remember glucose (which is created from the break down of carbohydrates) in excess will be turned into triglycerides. Creating triglycerides takes a lot of energy and is though to be one of the reaons you feel tired after a meal.
And for some reason people with autoimmune conditons seem to have low triglycerides.
What about HDL ?
HDL whist though of as thr god cholesterol if it is high especailly in an acute inflmmatory episode is protinflammatory especially if leves are high. HDL picks up fat to be metabolized.
HDL
high- excessive exercise, inflmmation
low- insulin, sednetary lifestyle, poor diet
Cholesterol (total)
high- thyroid, insulin, kidney disfunction, dehydration
low- liver dusfunction, inflmmation< malabsorption, anaemia
Triglycerides
high- glucose dysregulation, fasting?, thyroid, kidney issues
low- malabsorption, low intake, autoimmunity
Why would i need fat again?
We need saturated fat to give solid structures to out body ie cell walls, flexible arteries.
We should be having roughly 30% of our calories from saturated and unsaturated fats. If we don’t eat enough our liver overnight will get to work making it. But the trouble with this is our liver likes to make palmatic acid which is 100% saturated fat and it hardens arteries. And as mentioned earlier our body cant make Omega 3+ 6. We need to get that through our diet. Our immune cells also eat trans and hydrogenated fats as it treats them ike bacteria in the body and of course this can cause inflammation.
Turmeric to the rescue
Turmeric intake is one of the most effective ways to upregulate these pathways. Of converting linoleic acid to EPA and DHA. if you also add black pepper to tumeric it helps prevent glucoronidation 9degredation by the liver) of tumeric so it is effeciotve for longer.
WherE can i find the Omegas?
We need a blend of all omegas its just we hear about 3 and 6 the most.
Omega 6- high in grain fed meat
Omega 3- high in grass fed meat
Omega 9- olive oil and avocado
Omega 5- (is the best fat burner- strips fat our of the body) found in seed oil like pomegranate ( need the pulp). Pomegranate is a great antioxidant and is 10 x stronger than grape seed oil. This omega also stops Omega 6 going to arachadonic acid which is inflammatory.
Omega 7- seabuck thorn oil and macadamias, good for dry skin, dry hair, vaginal dryness, mucus membranes. Increases insulin sensitivity and stops insulin resistance.
CLA (conjugated linolenic acid)- very anti-inflammatory and causes P-Par gamma activation which protects against insulin resistance and inflammation. Making it good for a number of conditions like crohns, asthma, mucus membranes etc. It also helps stop the negative effects of cortisol and helps preserve muscle and is found in Safflower oil. It stimulates apoptosis of fat cells and stops fat cells expanding and even assisting fat cell emptying (lipolysis).
MCT (medium chain triglycerides)- is used easily as energy and its best to use coconut oil over palm oil if you want to ingest it. MCT is harder for the body to store and is considered hyperthermic ( makes liver use fat and increases body heat as primary fuel). The problem is if you eat this and have high fat and high sugar in the diet - the sugar will take preference and so the body wont burn it.
What about coloured fat in my body?
Our body can sotre fat that people refer to in colours.
Brown fat- highly thermogenic
White fat- ‘dried’ fat
By stimulating P-Par we can convert more white fat into brown fat.
P-PAR alpha- good for fat burning
P-PAR beta- inhibits the release of sugar fromthe liver- keeps fat burning
P-PAR gamma- increases insulin sensitivity but tells body to stop storing fat as fat adn the burn it.